AR VR device
How might we design that novice users can easily adapt to AR/VR environments?

Exhibited in a VIP demo with a head-mounted AR device at the Mobile World Congress
The expected effect of 12 trillion, approximately 5% of sales.
Launched Gear VR - Basic interaction, Gallery, Setup application
MY ROLE
Led the project
Guided 3 visual designers and 2 interaction designers
Research, Design, Prototyping
Set blueprint, roadmap
Problem

For beginners, the current interactions are too difficult.
How can the computer illiterate learn to use AR VR?
Many people are curious about AR and VR, but there are learning curves for adapting to AR and VR environments.
"How can I wear this? How can I select that menu in front of me?"
"I'm curious about the new technology, but I don't want to study how to use it."
- User interview
Process
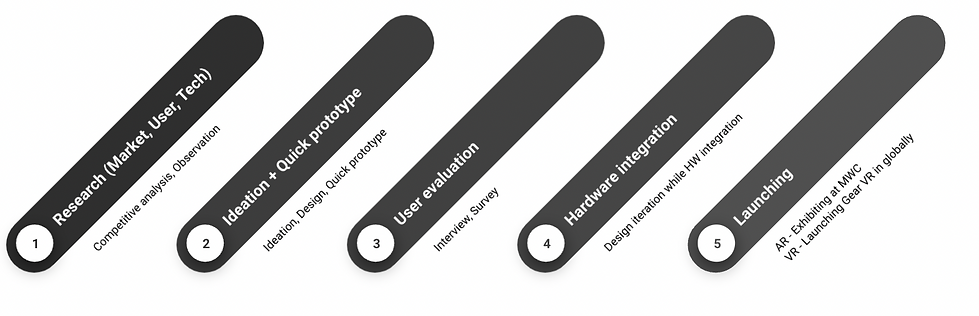
Research
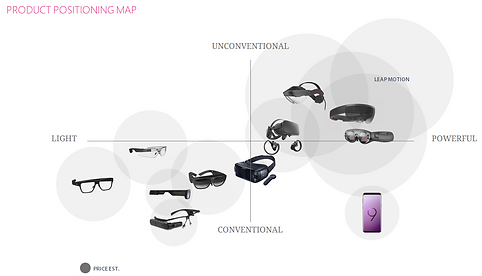
There were two types of AR devices in the market.
One is light and performs simple functions, and uses predictable interactions.
The other can perform powerful functions but it is heavy and users have to learn unfamiliar interactions (tap the Home button on their left wrist).
Obviously, unconventional interaction leads to confusion and difficulty to use.
Ideation + Quick prototype
From a business point of view, Samsung's AR devices are competitive in the market by providing powerful functions.
We need to find acceptable interactions.
Added and tested with many affordances to minimize user confusion and to learn interactions that users could most naturally accept using low-fidelity prototypes.
[ No image because it is a confidential project.]

User evaluation (with high-fi. prototype)
Users tend to imagine magical interactions before wearing the device but preferred conventional interactions after wearing it.
Moving the body beyond the elbow made users uncomfortable and embarrassed, and many users reported neck pain.
Most novice users were anxious when covering their eyes with the devices and looking around to understand the situation.
.png)
Launching
AR
Exhibited a VIP private demo at the Mobile World Congress.
The expected effect of 12 trillion, approximately 5% of sales.


VR
Launched a new Gear VR added a controller.
7 million in sales in the first quarter in France.

InsigHt #1.
" Where am I ? "
Show the location where users are at.
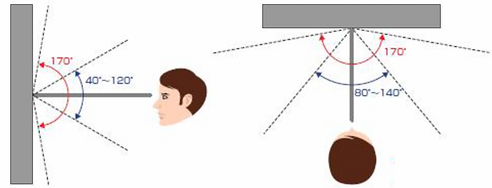
From user evaluation, I found that most novice users were looking around to understand the situation. They tended to look left and right. They got lost their location easily while navigating in unfamiliar environments.
I found previous studies that the human body is more accustomed to looking around while turning their heads in the left and right directions rather than up and down and that it is more accustomed to putting the user's gaze on the bottom rather than the top while wearing heavy head-mounted display equipment.
Added an indicator of controller
Added an indicator of the controller connecting the target object from the controller like a fishing line.
This let users know which UI components could be selected, wherever it was currently pointing at.
Because, unlike computer screens that use limited space, VR can position the screen 360 degrees.


Organized the horizontal screen
Arranged menu on the VR left and right. It let users easily find the menus.
According to existing research, it is structurally easier for people to move their gaze from side to side rather than up and down.
Because, structurally, it is easier for people to move their gaze from side to side rather than up and down.
Ease of movement: Side to side > Bottom > Up

VR Gallery (Media Viewer)
VR Internet browser
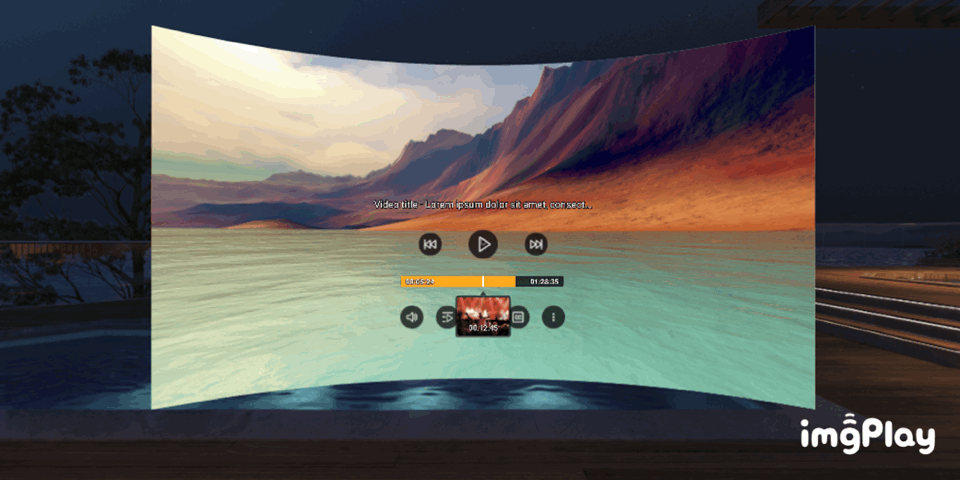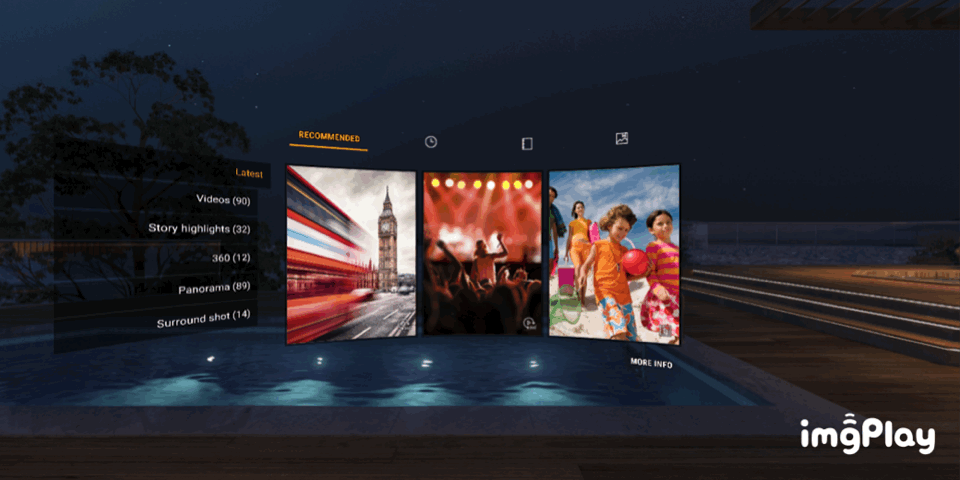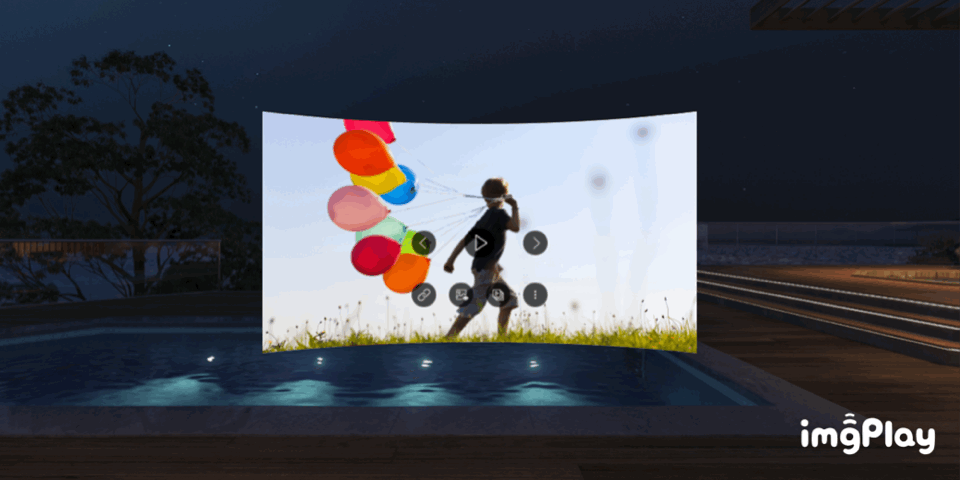
VR Gallery (Media Viewer, media from smartphone)
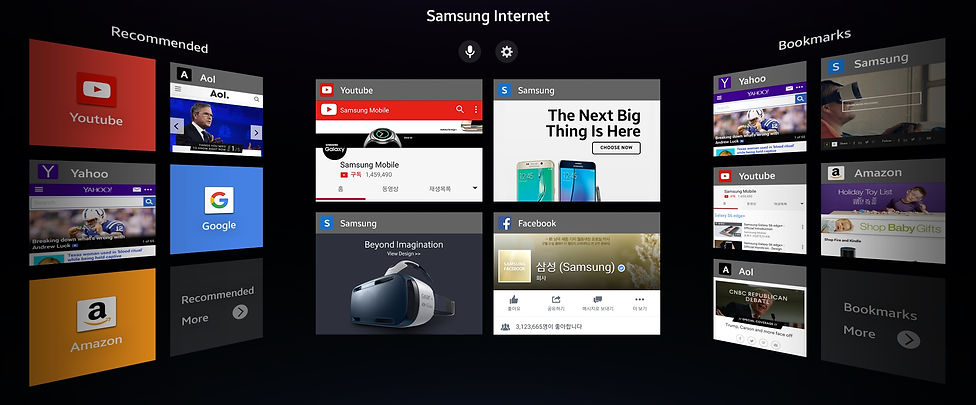
VR Internet browser
InsigHt #2.
"What's happening?" "Is it still happening?"
Show current status.
Found that users have a fear of blocking their view of the real world. Blocking all light from the outside was to provide a completely immersive experience and it was characteristic of head-mounted VR devices. But it was rather scary for users who try VR for the first time.
Loading indicator while launching
As soon as the user wears the VR, there is a slight delay before showing the landing screen.
I realized that people were mainly afraid because of the black screen at this time.
Before rendering the landing screen, I designed a screen using minimal performance to indicate to the user that the current VR is trying to render the landing screen.
Before, there was no screen. Just blackness.
After, users could check the loading bar while waiting for VR to render the landing page.


Added an animated Background
Added an animated wallpaper that gives a warm feeling to users who are using VR for the first time.
At the same time, it reduced dizziness by providing a sense of perspective to the user.
Iterated under the HW limits
The background image had to have the maximum effect with the minimum capacity because it had to minimize the impact on the performance of the VR device. For this, optimization through numerous iterations with the development team.
(China version only.)
Before
.png)
After
In addition,
Changed the background image for each season and time in order to minimize boredom due to long-term VR use.
Seasonal backgrounds




Can't describe my work in detail on the AR project because it is confidential.
Overall, I worked on designing and iteration basic interactions with the task of defining target users for new devices and defining key scenarios.

Patents
[WO2019103350A1] Apparatus and method for adaptively configuring user interface
Based on the height information of people wearing VR Head mounted display devices, I customized the distance of the buttons so that they could easily select a floating button with a light gesture. Because different people have different arm lengths, the positions of the buttons that feel appropriate may be different. For example. User (A), who is short, has a relatively short arm compared to user (B), who is taller, so the button provided to B is located closer than the button provided to A.

[WO2019164092A1] Electronic device for providing second content for first content displayed on display according to movement of external object, and operating method therefor
I admit that it is difficult to commercialize a cool design like a movie because AR technology can't yet keep up with the wide viewing angle of a person and make a machine as light as a human eye at an affordable price. However, under the given constraints, we have tried to provide the user interface in a better way to people. I studied how people prefer to communicate with AR devices, such as gestures, voice recognition, and physical buttons, and how information provided to the AR environment should be provided in what form and in what amount to differentiate from the real world and not bother users. As a result, AR glass, which was exhibited in a private mobile world congress, was designed to use the space where the user is located and display the contents in the appropriate size. For example, when a user looks at a blank wall, the movie is pasted on the wall to display, and when the user is watching TV, the content is displayed according to the TV size.